
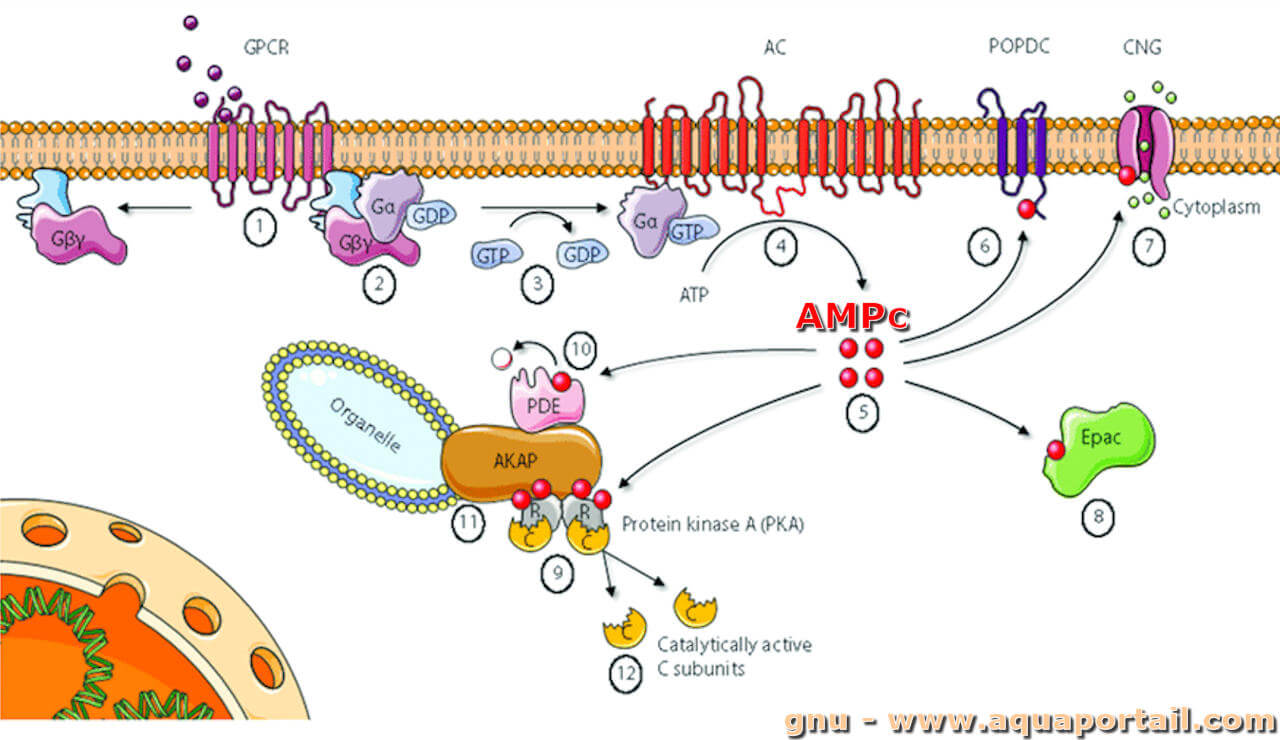
↑ Active-Site Structure of Class IV Adenylyl Cyclase and Transphyletic Mechanism. Second messengers include cyclic AMP, cyclic GMP. Hydrolysis of GTP switches off this signalling pathway.The alpha unit binds GDPand return to its resting state. Once activated these are linked to second messengers, agents that act within the cell to trigger a response. Phosphorylase a breaks down glycogen into glycogen residue and glucose 1-phosphate, releasing energy. The phosphorylated phosphorylase kinase converts phosphorylase b to a phosphorylated phosphorylase a. Another route: PKA phosphorylates phosphorylase kinase. PKA inactivates glycogen synthase a and converts it to a phosphorylated glycogen synthase b. PKA catalyses two different routes using phosphorylation. The binding causes a conformational change that releases and activates the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A (PKA). The cAMP binds to the regulatory subunit of cAMP dependent protein kinase A. This converts ATP to cyclic AMP ( cAMP). The alpha subunit with GTP binds to Adenylyl cyclase. The activated alpha subunit dissociates from the beta and gamma subunits of the G-protein. A conformational change is induced to the receptor causing the alpha subunit of trimeric G-protein to release GDP and bind GTP. Eprinephrine binds to transmembrane protein receptor ( G-protein linked receptor). The mechanism of eprinephrine (signalling molecule) binding to G-protein linked receptor (release of glucose in the "fight or flight" response) can display the roles of adenylyl cyclase and cAMP. This lowers cAMP levels even more.ĬAMP + H 2O -> 5'AMP + H +( proton) PK8 also has a negative feedback effect on PKA, decreasing adenylyl cyclase activity as a result. 
PK8 Phosphorylates Phosphodiesterase 3D, which lowers cAMP concentrations in the cells through hydrolysis. ĬAMP is also involved in EPAC ( Exchange proteins directly activated by cAMP) proteins. This is different in the cardiac muscle where epinephrine activates PKA which phosphorylates proteins/enzymes for increased contraction rate. For instance: in adipose tissue epinephrine results in higher cAMP thus increased PKA activity and then the PKA phosphorylates the appropriate enzymes resulting in trigylceride hydrolysis. Role of cAMPĪs mentioned above cAMP increases PKA activity, however, PKA has a different effect in the cells of different organs.
Role of cyclic amp in signal transduction free#
Types V and VI inhibited by Gαi and free Ca 2+. Types II, IV and VII can be activated by GαS and βγ These isoforms can be divided into three groups: Types I, II and VIII can be activated by GαS and Ca 2+/ calmodulin however ALSO can be inhibited by by ßy. The enzyme can exist in at least 9 isoforms that are regulated in different ways by different G protein-coupled receptors.

It is an integral membrane protein that has the structure of two bundles of six transmembrane segments and two catalytic domains that extend as loops into the cytoplasm, these catalytic domains are also the site of calmodulin binding.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
